🎥 Chapters
00:00 Understanding Calcific Tendinitis
0:37 Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy is the solution for Calcific Tendinitis
1:16 How ESWT works: breaking up scar tissue, adhesions, and calcification
1:51 Studies supporting ESWT: neovascularization, cartilage regrowth, inflammation reduction
2:37 Research on the Effectiveness of ESWT for Calcific Tendinitis
3:58 Success Rates of ESWT treatment compared to control groups for Calcific Tendinitis
4:25 Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) versus Conventional Surgery for Calcific Tendinitis
Shoulder Pain/Calcific Tendinitis and Shockwave Therapy
With Chiropractor in Los Gatos, San Jose, SF Bay Area, CA
Low energy focused shockwave therapy can help your calcific tendinitis. Whether it’s your supraspinatus tendon, biceps tendon, peroneal tendon, triceps tendon or others, extracorporeal shockwave therapy has your tendinitis covered.
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) isn’t just another treatment option; it’s a beacon of hope for those trapped in the grips of calcific tendinitis. Tendinitis can turn the simplest tasks into painful challenges. However, imagine the joy of raising your arm overhead without wincing in agony, swinging a golf club without fear of triggering excruciating pain, or simply reaching for a shelf without hesitating. ESWT has the power to transform everyday struggles into moments of triumph.
Science of Shockwave Therapy and Calcific Tendinitis
The science behind ESWT lies in its ability to harness the power of shockwaves to penetrate at precise depths into the affected tissue, disrupting and disintegrating calcium deposits while stimulating the body’s natural healing mechanisms. These shockwaves break up the rigid and brittle adhesions within the tissue, triggering a cascade of biological responses that promote tissue regeneration and repair. Studies have shown that ESWT increases blood flow to the affected area, stimulates the production of growth factors and cytokines, and enhances cell proliferation and tissue remodeling. The result is new collagen formation in the place of the scar tissue.
With each shockwave treatment, the burden of pain lifts, replaced by a renewed sense of vitality and possibility.
Is Shockwave Therapy Safe and Effective?
Moreover, low energy focused shockwave offers a non-invasive alternative to traditional treatments for calcific tendinitis, such as corticosteroid injections or surgical intervention. There are many studies that compare ESWT and other modalities and, whether it be cortisone injections, PRP, surgery, PT or others, ESWT comes out on top when it comes to efficacy and safety. Unlike invasive procedures that carry inherent risks and lengthy recovery times, ESWT is performed on an outpatient basis and boasts zero to minimal side effects. You will be able to resume your daily activities without skipping a beat. This makes ESWT a preferred choice for those seeking effective, yet gentle, solutions for calcific tendinitis, without compromising on safety or convenience.
Remember to chose low energy focused shockwave over an imposter called, “radial shockwave”. We have seen first-hand people come in our office after being bruised and battered by radial shockwave but never have this happen with the Piezowave low energy focused shockwave machine.
ESWT has the power to restore hope, vitality, and joy to those affected by calcific tendinitis. It’s not just about treating a condition; it’s about reclaiming a life filled with endless possibilities and moments of pure, unbridled happiness.
What Is Calcific Tendonitis of the Shoulder?

Frozen shoulder is adhesions (calcification) in the joint capsule of the shoulder. To break it down, calcific tendonitis is a calcification of the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles in your shoulder. It starts when there is inflammation from an injury or micro-trauma in the shoulder. The tendons heal by collagen forming cells called fibroblasts. With calcific tendonitis, on the other hand, fibroblasts are replaced with osteoblasts. Osteoblasts make a bone-like tendon. Therefore, these are bone forming cells that, literally, stimulate bone growth in the tendons of the shoulder.
It follows that when rotator cuff tendons calcify, the space between the tendon and the top of the shoulder (acromion) decreases and this causes impingement. This leads to further tendonitis and bursitis.
Calcific tendonitis tends to give some of the following SYMPTOMS:
- Decreased shoulder mobility
- Shoulder weakness
- Soreness that is worse in the morning
- Inflammation/swelling
- Shoulder makes sounds on movement
- Palpable painful lump on the tendon
- Pain moving arm overhead
7 Step Treatment For Calcific Tendonitis
- First of all, stop painful activities and apply heat (no anti-inflammatories)
- Most importantly, regain range of motion by breaking up calcifications with ESWT in our Los Gatos office
- Mobilize scapular movement with adjustments and exercises (see below for some exercises)
- While doing all of this, optimize spinal movement to restore neurology to shoulder
- At the prescribed time, strengthen rotator cuff muscles (see below)
- Now, build on your strength by adding challenging neuromuscular movements
- Finally, get back to your Bay Area life of fun and work
How Can Shockwaves Help My Shoulder Pain?
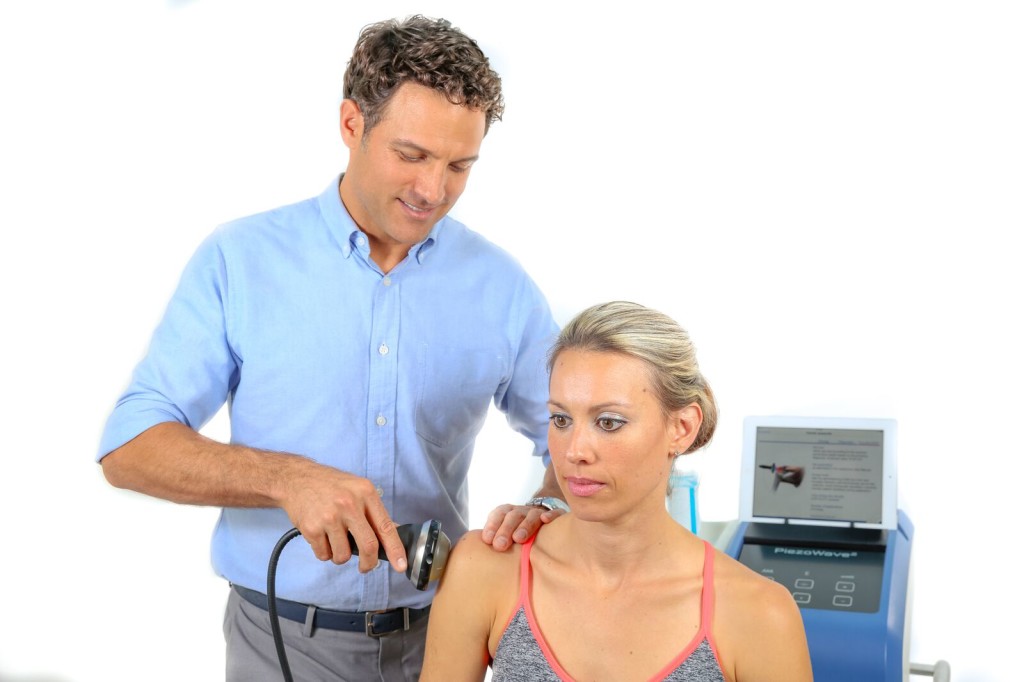

Dr. Fields of San Jose, CA demonstrating the use of ESWT for shoulder dysfunction
The Piezowave 2 sends acoustic waves traveling the speed of sound into your calcified tendon. The wave energy causes wave-like movement of the tissue. Because it is pliable, normal tissue just ripples.
However, calcified tissue breaks up like hard spaghetti that is bent. As a result, there is a cascade of events that spawn healing. First, new blood vessels come into the injured tendon (this is called angiogenesis). This allows your body to bring in healing properties and to flush out old inflammatory waste products. Most noteworthy is new collagen fibers are allowed to grow and flourish. Consequently, you are left with a stronger and more adaptable tendon that is better able to handle the mechanical stresses of life.
You can reach Dr Adam Fields for in-person (Los Gatos and San Jose, California) or telehealth appointments here.
About Chiropractor Dr Adam Fields
Dr Adam Fields is a practicing chiropractor in the Bay Area in Northern California and helps people daily in his office with many challenges that can be helped by shockwave therapy from tendinopathies, arthritis, cartilage regeneration, post surgical scar tissue, pelvic pain, altered biomechanics and more. He uses Endonasal Cranial Adjusting, the Muncie Technique, Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT), Class IV Laser Therapy, posture correction, lifestyle modification, muscle work, and other techniques to help his patients.
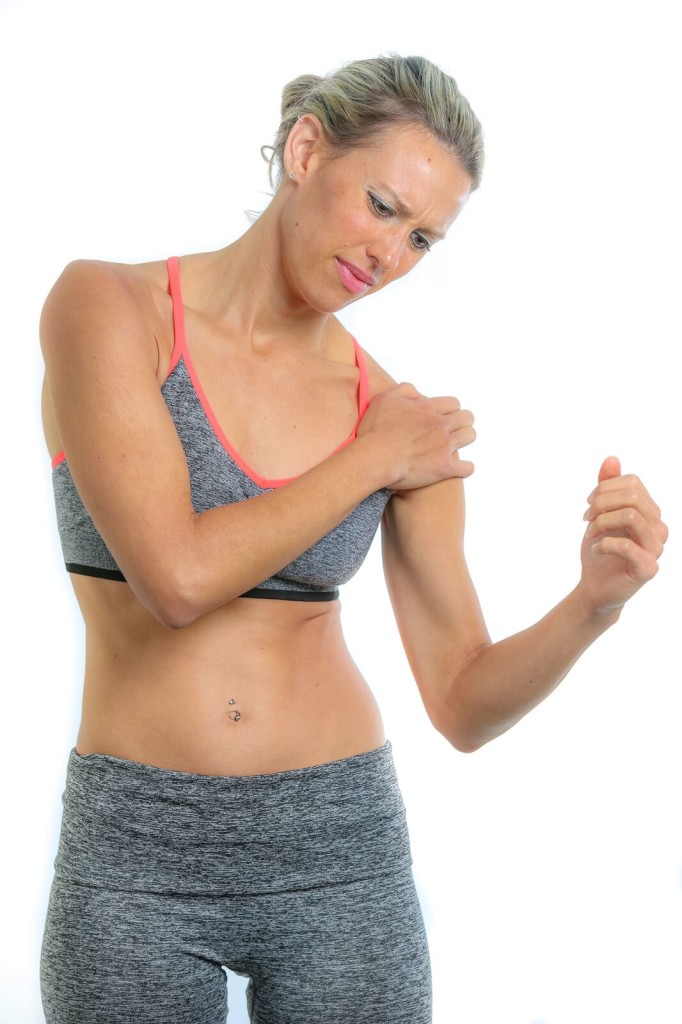



 Let’s be very clear, the research on calcific tendonitis and ESWT is excellent. The success rate is between 78% and 91%[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]. In a study with patients between 40 and 50 years of age, ESWT fragmented the calcifications which resulted in full range of motion and complete pain relief even 2 years post treatment [
Let’s be very clear, the research on calcific tendonitis and ESWT is excellent. The success rate is between 78% and 91%[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]. In a study with patients between 40 and 50 years of age, ESWT fragmented the calcifications which resulted in full range of motion and complete pain relief even 2 years post treatment [