🎥 Chapters
00:00 Osteoarthritis Symptoms and What Happens to Joints
0:41 Understanding Cartilage Degeneration
1:14 Exploring Bone Spurs in Osteoarthritis
1:40 Subchondral Sclerosis: The Third Hallmark in Osteoarthritis
2:02 Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) and Osteoarthritis: Breaking Scar Tissue, New Blood Flow, Collagen Growth
2:40 Research Evidence Supporting Shockwave Therapy for Osteoarthritis: Effectiveness Compared to Corticosteroid, Placebo etc.
4:06 Efficacy of ESWT in Knee Osteoarthritis
4:32 Meniscal Healing and Cartilage Regeneration In Osteoarthritis with Shockwave Therapy
5:37 Shockwave Therapy and TMJ Arthritis (TMJ)
Osteoarthritis and Shockwave Therapy
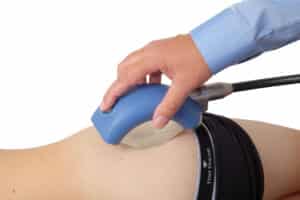
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) can help your osteoarthritis (OA). This therapy can reverse some of the key markers of degenerative joint disease (DJD). The wear and tear of joints in osteoarthritis can be reversed with shockwave therapy by initiating a regenerative cascade that cranks back time on osteoarthritic joints. Low-energy focused shockwaves from the Piezowave trigger a cascade of biological responses that reduce pain and help with functional improvement in affected joints (Wang et al., 2019). A study by Wang et al., ESWT demonstrated efficacy in ameliorating knee OA symptoms, enhancing joint function, and diminishing pain, thus underscoring its therapeutic potential (Wang et al., 2019). Shockwave for arthritis is a win in study after study.
The utilization of shockwave therapy goes beyond the confines of knee osteoarthritis. For instance, in hip osteoarthritis, ESWT has shown promise in mitigating pain and enhancing hip function, thereby offering a non-invasive adjunctive treatment option for individuals reluctant or ineligible for surgical intervention (Cacchio et al., 2016). With hand osteoarthritis, where conventional therapies may lack, ESWT emerges as a viable alternative, fostering improvements in grip strength, pain reduction, and overall hand function (Verstraelen et al., 2018).
ESWT exhibits therapeutic efficacy in addressing osteoarthritis of the spine. Lumbar facet joint osteoarthritis, characterized by chronic low back pain, pain while standing and functional impairment. Nevertheless, studies have elucidated the beneficial effects of ESWT in ameliorating pain and enhancing lumbar spine function, offering a promising avenue for individuals grappling with this debilitating condition (Lee et al., 2014). Furthermore, cervical facet joint osteoarthritis, a prevalent source of neck pain and stiffness, has been targeted with ESWT interventions, yielding improvements in pain scores and cervical range of motion, thereby enhancing the quality of life for affected individuals (Chen et al., 2019).
ESWT is an attractive therapeutic option for people suffering from osteoarthritis in peripheral joints, such as the ankle and shoulder. Ankle osteoarthritis, typified by pain, swelling, and impaired mobility, poses considerable challenges in management. However, studies have elucidated the efficacy of ESWT in assuaging pain, enhancing ankle function, and fostering improvements in quality of life for individuals grappling with this debilitating condition (Lee et al., 2016). Similarly, shoulder osteoarthritis, characterized by pain and restricted range of motion, represents a significant source of disability. Yet, ESWT interventions have demonstrated notable improvements in pain scores, shoulder function, and patient satisfaction, underscoring its utility in the multifaceted management of this condition (Wang et al., 2017).
How ESWT helps reverse key markers of joint degeneration.
2/ Cartilage Degeneration and Shockwave Therapy: Even more researched than bone spurs and shockwave therapy is tissue regeneration. Shockwave therapy helps regenerated collagen. How important is collagen to your tissues? Collagen provides structural support to the extracellular space of connective tissues, this is vital to regeneration and tissue strength. Due to its rigidity and resistance to stretching, it is the perfect matrix for skin, tendons, bones, and ligaments. For this reason, shockwave therapy falls under the category of regenerative medicine when it comes to arthritis and many other conditions like achilles tendonitis, plantar fasciitis, shoulder labral tears, tendinopathies and more.
3/ Subchondral Sclerosis and Shockwave therapy: Subchondral sclerosis is a condition characterized by the hardening (sclerosis) of the bone just below the cartilage surface within a joint and it is a hallmark of osteoarthritis. Like bone spurs, this hardening is a response to increased stress on the bone, often due to the loss of cartilage that cushions the joint. ESWT promotes neovasculartization, which improves blood flow to the subchondral bone and surrounding tissues, enhancing healing. ESWT can stimulate the cells involved in bone repair and remodeling, potentially reversing some of the sclerotic changes in the subchondral bone.
What about cortisone injections instead of ESWT for osteoarthritis?
Some people choose to get a cortisone shot for their arthritis joint. Injecting corticosteroids into the joint can reduce inflammation and swelling, providing relief from symptoms. However, cortisone is destructive to the cartilage and other structures of your joints. This can set the stage for weakness in the infrastructure of your tendons, ligaments and even bone. Yes, cortisone injections have been implicated in osteoporosis, tendon rupture and cartilage degeneration. With cortisone, there is a process that is activated called, “chondrocyte apoptosis”. This is a killing of the cells that make collagen. Why break down the joint even more when you can regenerate the joint with extracorporeal shockwave therapy?
Effectiveness of shockwave therapy
Call it ESWT, shockwave therapy or acoustic wave therapy, it is a versatile therapeutic modality for the management of osteoarthritis throughout the body. By harnessing the regenerative potential of shockwaves, ESWT can help bring new blood to the joint, decrease bone spurs and regenerate the collagen fibers. We have been practicing with it in our office since 2016 and the lives changed just keep stacking up.
MORE VIDEOS ON ESWT AND ARTHRITIS:
• Shockwave Therapy for Knee Arthritis
• Shockwave for Sacroiliac Pain
• Shockwave Therapy for Dog Injuries
You can reach Dr Fields for in-person (Los Gatos and San Jose, California) or telehealth appointments here.
Dr Adam Fields is a practicing chiropractor in the Bay Area in Northern California and helps people daily in his office with many challenges that can be helped by shockwave therapy from tendinopathies, arthritis, cartilage regeneration, post surgical scar tissue, pelvic pain, altered biomechanics and more.